Background:
- Over 130,000 amputations performed in 1997
- 68% of amputees carry diagnosis of diabetes
- Goals of amputation are to optimize function and minimize morbidity
Reasons to amputate:
- Peripheral vascular disease associate with diabetes
- Infection
- Trauma
- Frostbite
- Burn
- Tumor
Types of lower extremity amputations:
- Toe
- Ray – phalanges with all/part of metatarsal
- 5th ray most common, useful
- multiple ray amputations often narrow foot too severely
- Midfoot amputation
- Transmetatarsal
- Lisfranc – through tarsometatarsal joints
- Hindfoot amputation – Chopart
- talus and calcaneus preserved
- Syme
- talus and calcaneus removed with preservation of heel fat-pad to cover distal tibia/fibula
- fat-pad migration poses problem to future weight bearing
- Transtibial (below-knee amputation, BKA)
- most commonly performed major limb amputation
- 90% of amputees will successfully use a prosthesis
- Transfemoral (above-knee amputation, AKA)
- approx. 90% of amputees will walk with a prosthesis
- Knee Disarticulation
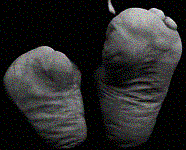
Transmetatarsal amputation on right foot and metatarsophalangeal toe amputation on left.
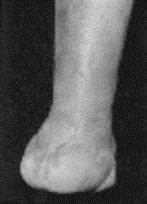
Chopart Amputation:
Talus and Calcaneus are retained.
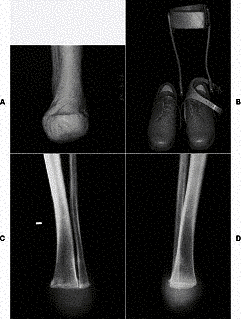
Syme Amputation
Considerations:
- Most distal level possible performed
- Adequate soft-tissue required for closure without tension
- Flap thickness and flap location
- Distal muscle stabilization
- Periosteum preservation (in adults)
- Neuroma prevention by clean transection of major nerves
- Early post-op ambulation with use of rigid dressings (casting)
Complications & Outcomes:
- Wound failure – wound healing is often complicated by diabetes and vascular disease
- More proximal amputations required in 5-10% of cases
- Infection – predisposed by amputation of infected or traumatic limb
- Phantom sensation
- Almost universal among amputees
- Telescoping = sensation that amputated limb is retracting toward stump
- Phantom pain
- Experienced by 60-70% amputees
- Many treatments described, including psychological support.
- Back Pain
- As or more common than phantom limb pain
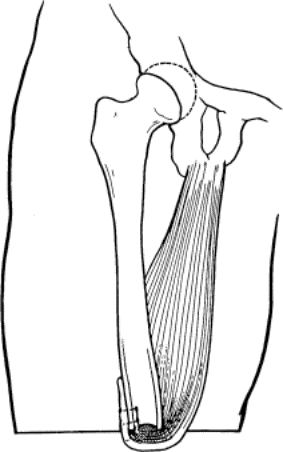
Transfemoral amputation: Gottschalk techique of anchoring of adductor magnus to lateral femur